New Pet Food Labeling Standards: What's New? Specialized News Column for Environmentalists and Environmentally Concerned Citizens On April 30, 2025, the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MOFA) issued a notice of partial amendment to the ‘Standards and Specifications of Feed, etc.’, establishing separate labeling standards for pet food (dog and cat). This is an important change for consumers' right to know and fair competition in the industry, as the legal distinction between pet food and livestock food is not clear. The revision strengthens the responsibility of manufacturers and salespeople to prove each statement on the packaging of pet food. In particular, it requires the type of food (complete food/other food) to be labeled, the content to be labeled when emphasizing specific ingredients and functions, the product name to be strengthened, the responsibility of specialized retail salespeople to be expanded, and the labeling conditions to be subdivided into ‘...
India-Pakistan conflict over water reflects a region increasingly vulnerable to climate change
In an unprecedented move, India recently suspended the 1960 Indus Waters Treaty with Pakistan, citing cross-border terrorism. This was one of a series of escalations between the two countries which now find themselves on the brink of war.
The treaty suspension reflects a growing regional trend: South Asian countries are increasingly treating water as a strategic asset rather than a shared resource amid rising mistrust, climate stress and geopolitical competition.
The region is home to nearly a quarter of the global population, and relies on huge transboundary rivers fed by Himalayan glaciers – the so-called “Third Pole” of freshwater reserves. A breakdown in water diplomacy could trigger environmental collapse, humanitarian crises and geopolitical instability. The weaponisation of water must be urgently addressed as a global climate justice issue.
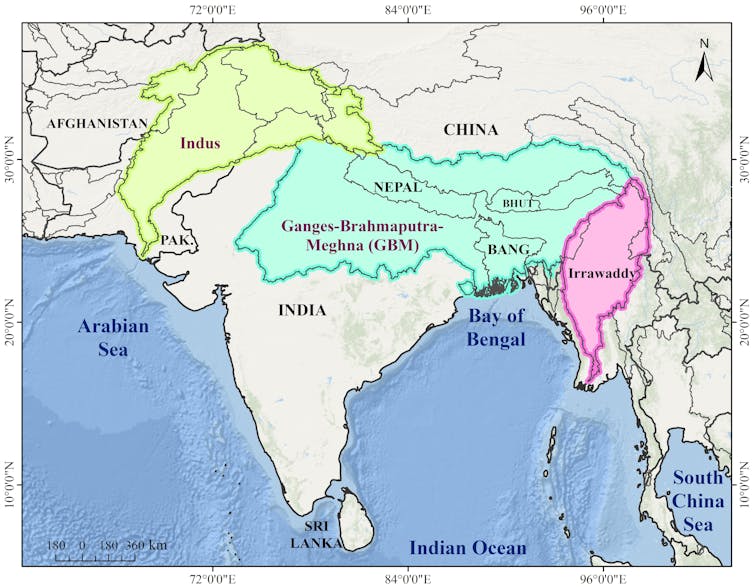
Major transboundary river basins of South Asia: Indus, Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna, and Irrawaddy. Mehebub Sahana, Author provided (no reuse)
A flashpoint occurred in August 2024 when devastating floods affected nearly 5.8 million people in Bangladesh. Some Bangladeshi officials accused India of releasing excess water from a large dam upstream without warning. India denied responsibility, citing extreme rainfall and standard dam operations. Nevertheless, the incident reignited longstanding tensions between the two countries.
Complicating matters further is China recently approving the construction of the world’s largest hydropower project on the Yarlung Tsangpo river in Tibet, which becomes the Brahmaputra in India. This massive project has raised alarm about China’s ability to exert control upstream, and the ecological risks for India and Bangladesh downstream.
China hasn’t signed formal water-sharing agreements with its neighbours, but its growing presence in regional water infrastructure signals a dramatic shift in south and east Asian hydro-politics.
Understand how AI is changing societyGet our newsletter
Climate change is making things worse
Recent climatic trends are making transboundary rivers an increasing focus of geopolitical friction. These trends include accelerated glacier melt, erratic monsoon patterns, and intensifying extreme weather.
While melting glaciers will temporarily boost the flow of rivers, the long-term prognosis is bleak. If emissions and warming trends continue, many glacier-fed rivers – including the Indus, Ganges and Brahmaputra – could see dramatically reduced flows by the end of the century. This will directly affect hundreds of millions of people who depend on them.
The crisis is being intensified by changes in the Himalayas. The region is warming faster than the global average, with a shift from snowfall to rainfall that disrupts the timing and volume of water that flows down from the mountains to the fields and cities below.
At the same time, unsustainable groundwater extraction has pushed South Asia’s reserves of underground water toward collapse, threatening both food and water security.
A dangerous precedent
A collapse or suspension of the Indus Waters Treaty could set a dangerous precedent. Importantly, the threat is less about India cutting off water flows – an unlikely and technically challenging act – and more about the erosion of trust, transparency and data sharing.
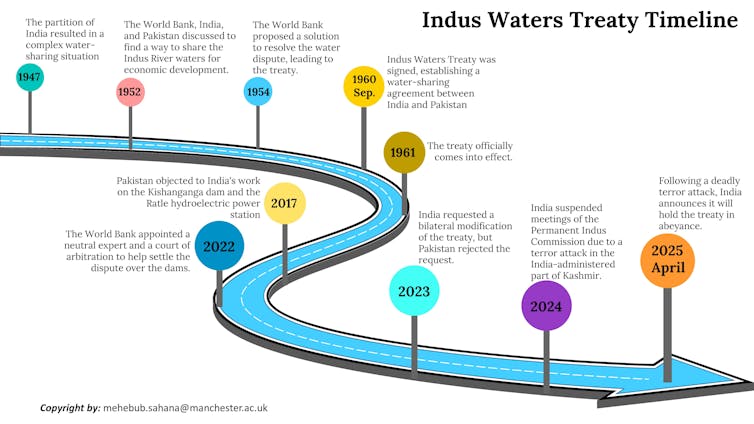
Indus Waters Treaty timeline. Mehebub Sahana, Author provided (no reuse)
One of the treaty’s most valuable features has been the routine sharing of data on things like water levels, river flow and dam operations. Pakistan needs this data to forecast floods and droughts, plan its irrigation, generate hydropower effectively and manage its drinking water, yet India is indicating it will no longer honour these obligations.
But India’s strained water relations are not limited to Pakistan. Bangladesh and Nepal have often felt sidelined or pressured in negotiations, and India’s indication that it may reconsider longstanding treaties raises concerns in both countries.
This is especially the case as the Ganges Water Treaty nears its 2026 expiration: the vast Ganges river flows through India and irrigates much of Bangladesh – and the treaty guarantees Bangladesh a minimum river flow.
Other key agreements, such as the Mahakali Treaty and Kosi river accord with Nepal, and the Teesta water-sharing deal with Bangladesh, remain largely unimplemented, breeding mistrust. These failures undermine confidence in regional water diplomacy and cast doubt on India’s commitment to equitable cooperation.
None of this is helped by India, Pakistan and Bangladesh all continuing to rely on outdated irrigation methods that mean they use more water than necessary. As climate change intensifies floods, droughts and glacial melt, there is an urgent need to reform existing water treaties to reflect present-day climate, hydrological and geopolitical realities.

Canals, like this one in Punjab, India, irrigate much of South Asia. Hussain Warraich / shutterstock
The Indus Waters Treaty, negotiated in the 1960s before the emergence of modern climate science, no longer accounts for these transformations. Indeed, most water treaties in the region remain rooted in technocratic, engineering-centric frameworks which fail to address extreme climate variability and its cascading impacts.
The upcoming expiration of the Ganges Water Treaty, and the pending negotiation of other basin agreements, present a critical opportunity to rethink water governance in South Asia.
Though the Indus flows through India before Pakistan, in other basins, India is downstream. This is the case with the Brahmaputra, where it demands upstream cooperation from China.
Undermining the Indus treaty could weaken India’s own position in future negotiations and strain its relations with Nepal and Bangladesh, while giving China more influence in South Asian hydro-politics. China is already expanding its footprint by offering billions in loans to Bangladesh and strengthening ties with Nepal, particularly around water infrastructure.
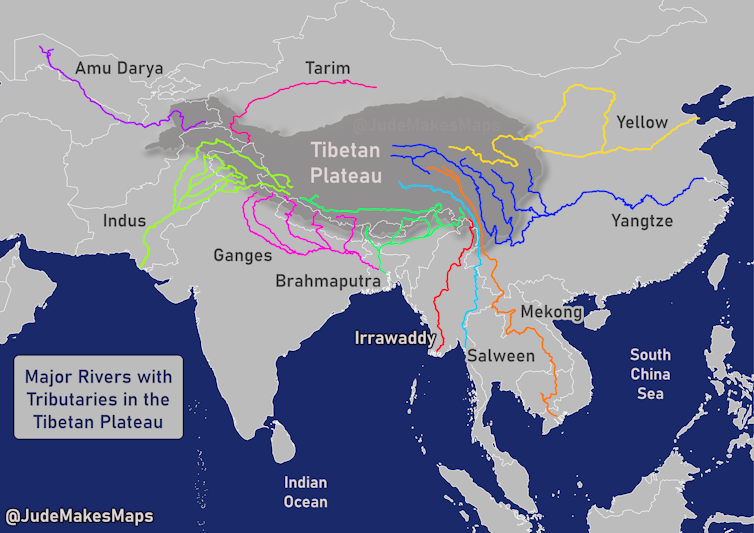
Many of the world’s largest rivers begin in the Himalayas or the Tibetan Plateau. JudeMakesMaps, CC BY-SA
Weaponising water is a perilous strategy that may backfire. The weakening of water diplomacy in South Asia is not just a regional threat; it endangers global climate security.
In the face of escalating climate change impacts and recurring disasters, updating transboundary agreements like the Indus Waters Treaty, Ganga Water Treaty, and Kosi and Teesta accords is no longer optional – it is an urgent necessity with enormous consequences.
댓글
댓글 쓰기